
Note: The model in the example also requires the Particle Tracing Module. The effect of the blade velocity on the compression factor is shown using a Parametric Sweep.
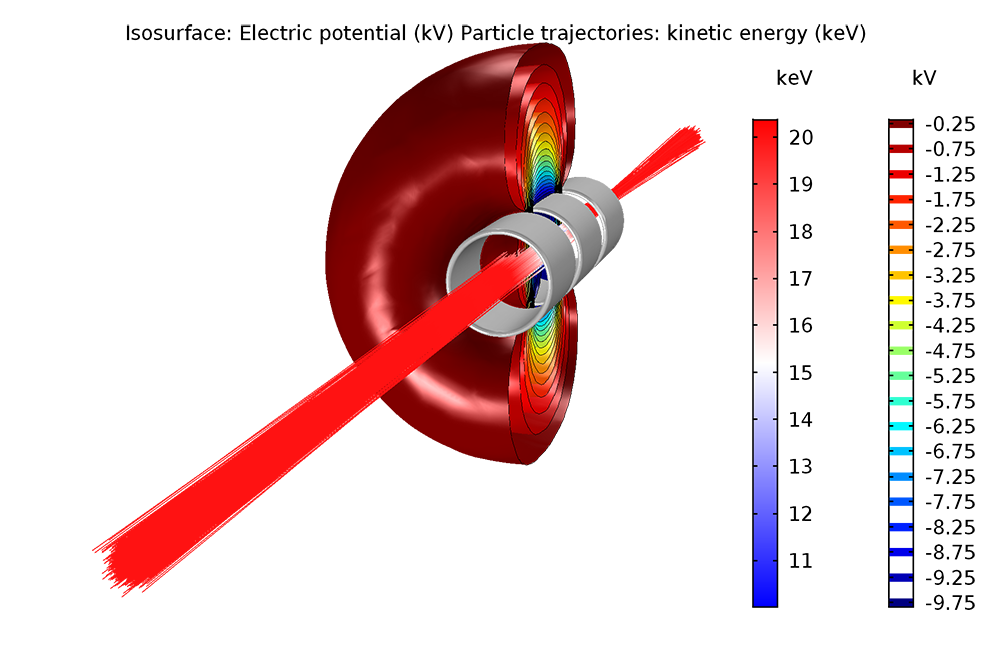
Updated Support for New CAD File Format Versions. The model uses the new Rotating Frame feature, which applies centrifugal and Coriolis forces to the particles, allowing the trajectories to be computed in a noninertial frame of reference that moves with the rotating blades. For users of the Design Module, COMSOL Multiphysics ® version 5.3a extends support to new versions of certain CAD file formats. In this example, the trajectories of gas molecules are computed in the empty space between two rotating blades of a turbomolecular pump.
For turbomolecular pumps, in which the blades move at speeds comparable to the thermal speed of the gas molecules, a Monte Carlo approach is needed. Learn more about these new features in the Particle.

Suspension concentration is assumed to be on the lower per-THOUSAND (not percent) range.
#PARTICLE TRACING MODULE COMSOL 5.3 FREE#
The Free Molecular Flow interface available in the Molecular Flow Module is an efficient tool for modeling extremely rarefied gases when the gas molecules move much faster than any geometric entities in the domain. For users of the Particle Tracing Module, COMSOL Multiphysics version 5.5 brings new virtual mass and pressure gradient forces for the Particle Tracing for Fluid Flow interface, improved acoustophoretic force functionality, and more ways to release particles with a size distribution. Comsol Multiphysics - Particle Tracing Module: - Particles do not displace the fluid they occupy. Number density (1/m 3) inside a vacuum chamber fed with a small capillary tube, modeled using half the geometry with a Plane Symmetry.Īpplication Library path for an example that uses the Plane Symmetry boundary condition: Molecular_Flow_Module/Industrial_Applications/differential_pumping New Tutorial: Turbomolecular Pump


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
